
This process leads to the expression for the moment of inertia of a point mass. This provides a setting for comparing linear and rotational quantities for the same system. If the mass is released from a horizontal orientation, it can be described either in terms of force and accleration with Newton's second law for linear motion, or as a pure rotation about the axis with Newton's second law for rotation. Momentum is simply defined for an object as the product of the object’s mass and velocity.Moment of Inertia Rotational and Linear ExampleĪ mass m is placed on a rod of length r and negligible mass, and constrained to rotate about a fixed axis. The main difference between inertia and momentum is that inertia does not depend on the object’s velocity, whereas momentum depends on the object’s velocity.
How does momentum differ from inertia?. The moment of inertia is proportional to R 2 hence, to increase I at fixed mass, theĭA: 60 PA: 10 MOZ Rank: 11 Up or Down: Up (e) place part of the body farther from the axis. To increase the moment of inertia of a body about an axis, you must (a) increase the angular acceleration. How do you determine the moment of inertia? Ĭalculate the rotational inertia or the moment of inertia by multiplying the mass of the object with square of the distance between the object and the axis, the radius of rotation.ĭA: 62 PA: 54 MOZ Rank: 65 Up or Down: Up. And, the moment of inertia represents the effort we need to get something to change its angular velocity.ĭA: 31 PA: 32 MOZ Rank: 40 Up or Down: Up 
The quantity mr 2 is called the moment of inertia, I. This is an important result because it relates to torque and angular acceleration.
Moments of Inertia – concepts & definition. Moments of Inertia - formulas & sample numerical physicsteacher.in. Because r is the distance to the axis of rotation from each piece of mass that makes up the object, the moment of inertia for any object depends on the chosen axis.ĭA: 85 PA: 81 MOZ Rank: 70 Up or Down: Up for all the point masses that make up the object. We defined the moment of inertia I of an object to be. 10.5 Calculating Moments of Inertia – University Physics opentextbc.ca. ĭA: 87 PA: 98 MOZ Rank: 27 Up or Down: Up For a point mass, the moment of inertia is just the mass times the square of perpendicular distance to the rotation axis, I = mr 2. 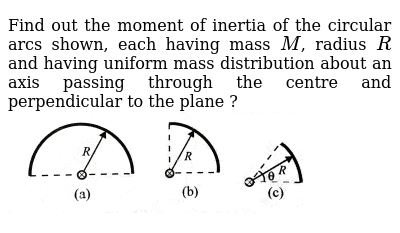
The moment of inertia must be specified with respect to a chosen axis of rotation. That measurement is calculated based upon the distribution of mass within the object and the position of the axis, meaning that the same … Occupation: Math And Physics ExpertĭA: 30 PA: 76 MOZ Rank: 53 Up or Down: Up
The moment of inertia of an object is a calculated measure for a rigid body that is undergoing rotational motion around a fixed axis: that is to say, it measures how difficult it would be to change an object's current rotational speed. What Is Moment of Inertia in Physics? - ThoughtCo. Author: OpenStax Publish Year: 2016ĭA: 10 PA: 83 MOZ Rank: 76 Up or Down: Up From this result, we can conclude that it is twice as hard to rotate the barbell about the end than about its center. In the case with the axis at the end of the barbell-passing through one of the masses-the moment of inertia is. 10.5 Calculating Moments of Inertia – General Physics ucf.edu. Calculate the moment of inertia of the remaining disc about an axis perpendicular to the plane of. Moment of Inertia - Formulas, MOI of Objects [Solved …. The moment of inertia (I) is mostly specified based on the distribution of mass in the body with …ĭA: 78 PA: 13 MOZ Rank: 50 Up or Down: UpĮquation of the moment inertia becomes: 2 2 x 222 I y dA y d dA y dA y dA d dA c cc ³³ ³ ³ ³ In simple terms, it is the opposition that the body exhibits to the change in rotation about an axis which may further be internal or external. Moment of inertia from a Physics point of view is basically a quantitative measure of the rotational inertia or the angular mass of a body. Moment of Inertia - Moment of Inertia Units, Moment Of.  s ) in imperial or US units.ĭA: 63 PA: 64 MOZ Rank: 53 Up or Down: Up. m ) in SI units and pound-foot-second squared (lbf. Moment of inertia may be expressed in units of kilogram metre squared (kg The amount of torque needed to cause any given angular acceleration (the rate of change in angular velocity) is proportional to the moment of inertia of the body.
s ) in imperial or US units.ĭA: 63 PA: 64 MOZ Rank: 53 Up or Down: Up. m ) in SI units and pound-foot-second squared (lbf. Moment of inertia may be expressed in units of kilogram metre squared (kg The amount of torque needed to cause any given angular acceleration (the rate of change in angular velocity) is proportional to the moment of inertia of the body. #Find mass moment of inertia of a circle free#
When a body is free to rotate around an axis, torque must be applied to change its angular momentum.




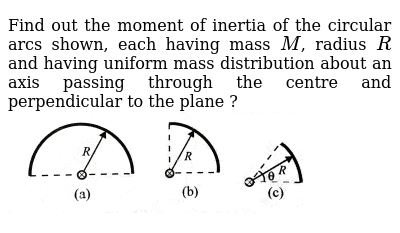



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
